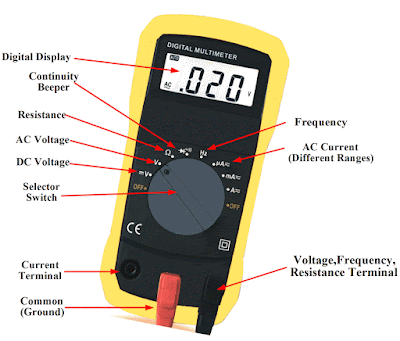
Components of a Multimeter
1.Shows the measurement readings.
2. Dial/Selector Knob:
Allows you to select the type of measurement (voltage, current, resistance, etc.) and the range.
3. Ports:
Where the test leads are connected. Common ports are:
-COM (Common):
The negative or ground terminal.
-VΩmA:
Used for measuring voltage, resistance, and small currents.
10A:
Used for measuring higher currents.
4. Test Leads:
Probes that connect the multimeter to the circuit or component being tested.
1. Measuring Voltage:
- DC Voltage (V—), Used for measuring direct current voltage (e.g., batteries, DC power supplies).
AC Voltage (V~):
Used for measuring alternating current voltage (e.g., household )
1. Turn the dial to the appropriate voltage setting (DC or AC).
2. Plug the black test lead into the COM port and the red test lead into the VΩmA port.
3. Touch the black probe to the negative side of the circuit and the red probe to the positive side.2. Measuring Current:
DC Current (A—): Measures direct current.
AC Current (A~): Measures alternating current.
4.De-energize Circuits.
Always de-energize circuits before measuring resistance or continuity.
5. Inspect Leads:
Regularly check test leads for damage and replace them if necessary.




.webp)
No comments:
Post a Comment